Introduction
htop is a tool in Linux that allows you to monitor your system’s vital resources and the processes (applications) that are running in near real-time. Because it is not included by default you will have to install it but don’t fret, it’s just a command away! We’ll cover how to install it in the popular distribution that Cloud Servers offers.
Before we begin, this article makes a few assumptions:
- You have completed the associated Setup Guide for your Cloud Server
- You are logged in as a non-privileged user with sudo permissions
- You are familiar with using Linux tools, such as top.
Installing in CentOS/RHEL/Fedora
To install htop all you have to type is:
# sudo yum install htop
This will start the YUM package manager and install htop for you. Once it is installed just type htop to start.
Installing in Ubuntu/Debian
To install htop all you have to type is:
# sudo aptitude install htop
This will start Aptitude and begin the installation. Once installed just type htop to view the application.
Using htop
Our demonstration was created using an Ubuntu 8.04 server. Your system may look slightly different.
Main Screen
When you start htop you will see a screen like the following — this is the main screen when loading htop.
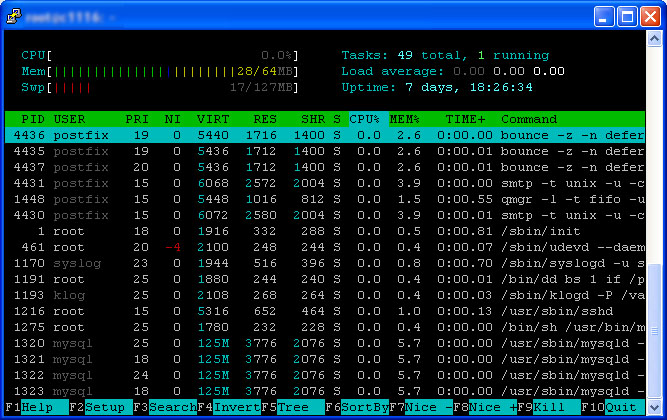
To get around in this screen you will have several F-keys that you can press (see the bottom of the window) along with using your left/right arrow keys to pan across the process list. Up/down arrow keys will scroll through each line item process in the list to perform particular actions.
Getting Help
If at any time you need assistance or you just forgot that key command you can press the F1 key. This will bring up a help screen with the keyboard commands. It also gives some explanation of the interface design and the particulars of that. Because of the different versions shipped with each distribution some key commands may not be available or the screen layout might be slightly altered.
Simply press a key to get out of the help screen.
Setup
If you press the F2 key you will be shown a setup screen. This will allow you configure the screen layout (what metrics are shown), what types of processes to show, etc. We won’t cover much more than this on the topic because each person has their own requirements of what to see. We find that the default layout is sufficient for most users.
To exit setup simply press the F10 key. Unfortunately this key does not always show up on each setup screen.
Searching
If you press the F3 key you will be given a search prompt at the bottom of the screen. Simply type in the item you would like to search for and it will, in real-time, take you to a matching process in the process list. In our example image we have searched for mysql and it took us to the first mysqld process.
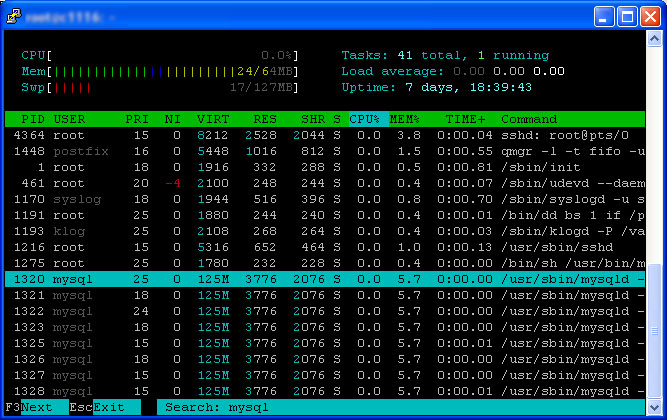
You can press the F3′ key to find the next matching process or just press ESCape to quit the search.
Tree View
Maybe seeing the process list by process number or CPU usage isn’t what you really want to see. Maybe you want to see what processes are child’ processes of a single process; this might be useful for application services such as Apache. You can press the F5 key and it will sort the process list in a tree. See the image below for an example.
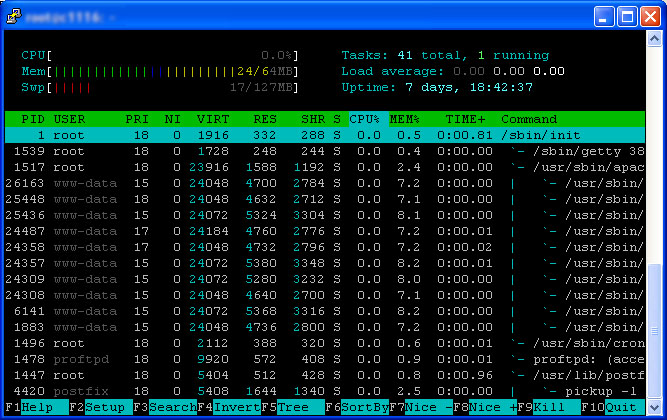
To get out of the tree view just press the F5 key again.
Sorting
By default htop will start out sorting by CPU usage. Maybe you’d like to see the list sorted by memory usage, PID number, or even by the user that executed them. You can easily do this by pressing F6 for the SortBy function. A list will be presented, on the left side, with items that you can sort the list by. Simply press the up/down arrows on your keyboard to scroll through the list and press Enter to select the item. You will notice that the column you have chosen to sort by will turn to a different color (cyan in our example) to notate that you are sorting by that column.
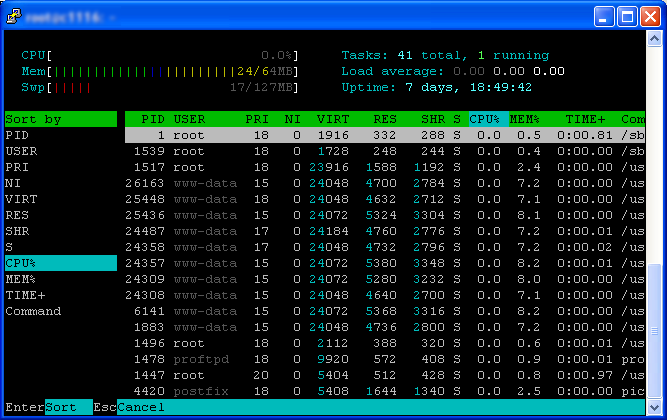
If you would like to go back to the default value simply press F6 and select CPU%.
Killing Processes
If you run htop as a privileged/root-level user you may use the Kill button to kill processes. To kill a process use the up/down arrow to find the process you would like to kill and then press the F9 key.
Quit
To quit htop just press the F10 key.
Conclusion
Hopefully this tutorial has allowed to become a little bit more familiar with tools that are available to manage your Cloud Server.
Disclaimer
htop is another tool to add in your system administrator toolkit and is simply meant to compliment the original topprogram. Because htop is not included by default with most distributions it is not supported by Cloud Servers and will be used at your own risk.
Views: 150
